Unveiling Roman Dynasties: A Comprehensive List takes us on a fascinating journey through the intricate web of Roman rulership. Did you know that the Roman Empire spanned over 500 years, with 83 emperors ruling in succession? This comprehensive list provides a valuable resource for those seeking to understand the rise and fall of Roman dynasties and their lasting impact on history.
Delving into Unveiling Roman Dynasties: A Comprehensive List, we uncover the rich tapestry of Roman history. From the legendary Julius Caesar to the enigmatic Augustus, this curated collection unveils the achievements, conflicts, and legacies of the Roman emperors. With insightful commentary and meticulously researched information, readers gain a deeper understanding of the dynamics that shaped the Roman Empire. As we delve into this comprehensive list, we discover the complexities of Roman governance and the enduring allure of ancient Rome.
Discover the fascinating history of the Roman dynasties with our comprehensive list. From the famous Julio-Claudian dynasty to the powerful Flavian dynasty, this list unveils the rulers who shaped ancient Rome. Explore the achievements and legacies of each dynasty, from the mighty reign of Augustus to the infamous debauchery of Nero. Dive into the intricacies of Roman politics and power as you delve into our meticulously curated list of Roman dynasties.
Contents
Unveiling the Roman Dynasties: A Comprehensive List
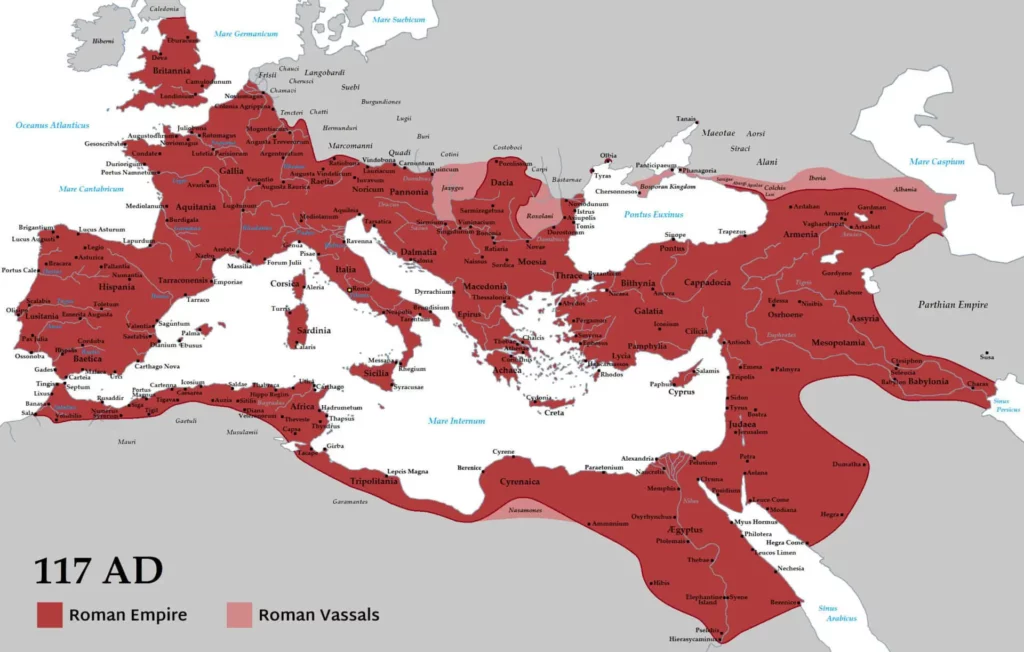
The Roman Empire, one of the greatest civilizations in history, spanned over a thousand years and witnessed the rise and fall of various dynasties. Understanding these dynasties is crucial to comprehending the political, social, and cultural aspects of ancient Rome. In this comprehensive list, we will explore the major Roman dynasties and their contributions to the growth and development of the empire.
The Julio-Claudian Dynasty
The Julio-Claudian Dynasty, established by Augustus Caesar in 27 BC, marked the beginning of the Roman Empire. This dynasty was named after its two prominent emperors, Julius Caesar and Augustus. Julius Caesar, a military genius and politician, played a crucial role in transforming the Roman Republic into an empire. His adopted son, Augustus, became the first Roman Emperor, initiating an era of peace and stability known as the Pax Romana.
Under the rule of the Julio-Claudian Dynasty, the Roman Empire expanded its territory, constructed magnificent buildings, and witnessed significant social reforms. However, this dynasty also faced internal political conflicts and power struggles. The reign of emperors like Caligula and Nero was marked by extravagance, corruption, and brutality.
In the end, the Julio-Claudian Dynasty came to an end with the suicide of Nero in 68 AD. Despite its shortcomings, this dynasty established the foundations of the Roman Empire and set the stage for the future dynasties that would shape the course of Roman history.
Augustus Caesar
Augustus Caesar, the first emperor of the Roman Empire, played a pivotal role in establishing the Julio-Claudian Dynasty. Born as Gaius Octavius, he rose to power after the assassination of his great-uncle, Julius Caesar. Augustus brought stability to Rome after years of internal conflicts and civil wars.
During his reign, Augustus implemented significant administrative reforms, restructured the Roman Senate, and instituted a strong imperial bureaucracy. He also initiated ambitious public works projects, including the construction of temples, aqueducts, and roads. The reign of Augustus Caesar marked a period of peace and prosperity in Rome, known as the Pax Romana.
Augustus Caesar’s contributions to Roman society were immense, and his impact on the empire’s governance still influences political systems today. His rule set a benchmark for future emperors, and the Julio-Claudian Dynasty owed much of its initial success to his visionary leadership.
Nero
Nero, the last emperor of the Julio-Claudian Dynasty, is often remembered for his tyrannical rule and extravagant lifestyle. During his reign, Rome experienced a devastating fire that destroyed a significant portion of the city. However, Nero is believed to have played a role in rebuilding the city and initiating urban planning efforts.
Despite his initial popularity, Nero’s rule was marked by increasing cruelty and debauchery. He is infamous for persecuting Christians and executing prominent figures, including his own mother, Agrippina. Nero’s reign ultimately ended in chaos and rebellion, leading to his suicide in 68 AD.
Though Nero’s rule was marred by brutality and excess, his architectural projects and artistic endeavors left a lasting impact on Rome. He was known for his enthusiasm for the arts and is considered one of the first Roman emperors to actively engage in cultural pursuits.
The Flavian Dynasty
The Flavian Dynasty, established by Vespasian in 69 AD, marked a new phase in Roman history after the turbulent period that followed Nero’s death. The dynasty consisted of Vespasian and his two sons, Titus and Domitian. The Flavian emperors sought to restore stability and order in Rome and reinforce the power of the imperial office.
Under the Flavian Dynasty, the Roman Empire witnessed significant military victories, including the suppression of the Jewish rebellion in Jerusalem. The construction of iconic structures like the Flavian Amphitheatre, commonly known as the Colosseum, and the renovation of the Roman Forum were also undertaken during this period.
While Vespasian and Titus were well-received by the Roman populace for their military achievements and public works, Domitian’s reign was marked by increasing autocracy and a decline in social and economic conditions. Domitian’s oppressive rule eventually led to his assassination in 96 AD.
Vespasian
Vespasian, the founder of the Flavian Dynasty, was a skilled military commander who emerged as the emperor after the chaos following Nero’s death. He focused on restoring financial stability to Rome and instituted various fiscal reforms.
One of Vespasian’s most significant accomplishments was the construction of the Colosseum, a magnificent amphitheater that became a symbol of Roman grandeur and entertainment. Under his rule, Rome experienced economic prosperity and an expansion of public infrastructure.
Vespasian’s pragmatic approach and ability to bring stability to Rome laid the foundation for the Flavian Dynasty’s success. His reign marked a transition from the chaos of the previous years to a period of consolidation and progress.
Titus
Titus, the eldest son of Vespasian, succeeded his father as the emperor of Rome. His brief reign of just two years was marked by significant disasters, including the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, which buried the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
Despite these challenges, Titus is remembered for his generosity and compassion towards the people of Rome. He provided relief to those affected by natural disasters and worked towards improving the living conditions of the lower classes.
Titus’s reign was cut short by his untimely death, but his show of benevolence and empathy during his short rule earned him a place in Roman history as a popular and well-regarded emperor.
The Severan Dynasty
The Severan Dynasty, established by Septimius Severus in 193 AD, saw Rome undergo significant changes. Septimius Severus and his descendants aimed to consolidate power and strengthen the empire’s defenses against external threats. The dynasty lasted until 235 AD.
Under the Severan emperors, the Roman Empire witnessed military campaigns aimed at establishing control over the eastern regions, including Mesopotamia and Parthia. The dynasty also introduced various social reforms to address growing economic disparities and stabilize the empire.
However, the latter years of the Severan Dynasty were marked by internal strife and power struggles among family members, leading to a decline in stability and governance. The assassination of Alexander Severus in 235 AD marked the end of the dynasty and plunged Rome into a period of crisis known as the Crisis of the Third Century.
Septimius Severus
Septimius Severus, a distinguished military commander, seized power and established the Severan Dynasty. He aimed to restore stability to Rome and strengthen the empire’s borders.
During his reign, Septimius Severus undertook military campaigns against rival factions and expanded the empire’s territory. He implemented various legal and administrative reforms and offered incentives to the army to maintain their loyalty.
Septimius Severus’s reign brought a semblance of stability to Rome, but his successors faced challenges in maintaining unity and control. Nevertheless, his reign established the foundation for the Severan Dynasty and set the stage for the political and military developments that followed.
Caracalla
Caracalla, the eldest son of Septimius Severus, became the emperor of Rome after his father’s death. He is noted for his military campaigns and the construction of large public baths, known as the Baths of Caracalla.
However, Caracalla’s reign was marred by his reign of terror and political purges. He ordered the assassination of his political rivals and instigated conflicts within the empire. His tyrannical rule led to his assassination in 217 AD.
Despite the controversies surrounding Caracalla, his reign witnessed significant developments in art, architecture, and infrastructure. The Baths of Caracalla are a testament to his grand architectural projects and his ambition to leave a lasting legacy.
The Legacy of Roman Dynasties
The Roman dynasties, including the Julio-Claudian, Flavian, and Severan dynasties, left an indelible mark on ancient Roman history. Through their military conquests, architectural achievements, and social reforms, these dynasties shaped the destiny of the Roman Empire.
The Julio-Claudian Dynasty laid the foundations of the Roman Empire and established the imperial office. The Flavian Dynasty brought stability and undertook significant construction projects that still stand today as symbols of Rome’s grandeur. The Severan Dynasty aimed to strengthen the empire against external threats and introduced social reforms to address internal issues.
While each dynasty had its successes and failures, their rule played a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of Rome. They set precedents for future emperors and laid the groundwork for the cultural and political legacy that continued long after their reigns.
Unveiling Roman Dynasties: A Comprehensive List
When exploring the rich history of ancient Rome, understanding the dynasties that ruled the empire is essential. From the founding of Rome to its fall, several dynasties shaped the course of Roman history.
The first dynasty was the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which began with Emperor Augustus and lasted until the death of Emperor Nero. This dynasty witnessed significant expansion of the empire and cultural developments.
The next dynasty was the Flavian dynasty, which started with Emperor Vespasian and ended with the reign of Emperor Domitian. This period was marked by political stability and military conquests.
The adoptive Antonine dynasty followed, with emperors such as Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius, and Commodus. This era saw advancements in architecture and law.
The Severan dynasty, starting with Emperor Septimius Severus, saw a mixture of military strength and internal conflicts, leading to the eventual decline of the empire.
The final dynasty before the fall of Rome was the Constantinian dynasty, founded by Emperor Constantine. This dynasty witnessed the establishment of Christianity as the state religion.
Exploring these dynasties provides a comprehensive understanding of the political and cultural transformations that occurred in ancient Rome. Each dynasty brought its unique contributions and challenges, shaping the empire’s destiny.
Key Takeaways: Unveiling Roman Dynasties: A Comprehensive List
- Rome had several dynasties that ruled over the centuries.
- The Julio-Claudian dynasty was the first Roman imperial dynasty.
- The Flavian dynasty followed the Julio-Claudian dynasty.
- The Severan dynasty marked the beginning of the Crisis of the Third Century.
- The Theodosian dynasty was the last dynasty to rule over both the Eastern and Western Roman Empire.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Roman Empire spanned centuries and was ruled by various dynasties. Here are some frequently asked questions about Roman dynasties and a comprehensive list to help you understand the rulers of ancient Rome.
1. Who were the Julio-Claudian dynasty?
The Julio-Claudian dynasty refers to the first five Roman emperors who ruled the Roman Empire, starting from Augustus Caesar, the adopted son of Julius Caesar. The dynasty included Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero. They were known for consolidating power and establishing a hereditary empire.
2. Which dynasty followed the Julio-Claudians?
The Flavian dynasty succeeded the Julio-Claudians. It began with the reign of Vespasian, who was succeeded by his sons Titus and Domitian. The Flavians were known for their military achievements, including the conquest of Jerusalem and the construction of the Colosseum.
3. Who were the Five Good Emperors?
The Five Good Emperors refer to the five Roman emperors who ruled from 96 to 180 AD, known for their competent and prosperous reigns. They were Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius. This period is considered a golden age of stability and expansion for the Roman Empire.
4. What was the rule of the Severan dynasty?
The Severan dynasty began with the reign of Septimius Severus, who became emperor in 193 AD. The dynasty included Severus’s sons Caracalla and Geta, as well as other short-lived emperors. The Severans focused on military expansion and strengthening the imperial administration.
5. How did the crisis of the third century impact Roman dynasties?
The crisis of the third century was a period marked by political instability and economic decline in the Roman Empire. It led to frequent changes in rulers and the emergence of numerous short-lived and competing dynasties. This period was characterized by civil wars, invasions, and overall instability in the empire.
To sum up, the Roman dynasties have played a crucial role in shaping the history of ancient Rome. This comprehensive list has provided a detailed overview of the various dynasties that ruled over Rome, showcasing their influence and impact on the empire. From the founding dynasty of the Julians to the final dynasty of the Valentinians, each dynasty had its unique characteristics and contributions.
By exploring this list, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the Roman Empire’s intricate political and social dynamics. From the early Republic to the mighty Empire, the Roman dynasties navigated through times of triumph and turmoil, leaving an indelible mark on world history. Let this comprehensive list be a gateway to unravel the fascinating stories behind each Roman dynasty and the empire they ruled.